How Does PROFIBUS Work?
PROFIBUS (Process Field Bus) is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation systems. It facilitates the exchange of data between controllers (such as PLCs) and field devices (such as sensors and actuators) within a network. Understanding how PROFIBUS operates is essential for setting up and maintaining efficient and reliable automation systems.
Introduction to PROFIBUS
PROFIBUS is a fieldbus communication standard that was developed in the late 1980s and has since become a key technology in industrial automation. It supports both high-speed communication for discrete automation (PROFIBUS DP) and robust communication in process automation environments (PROFIBUS PA).
PROFIBUS Network Structure
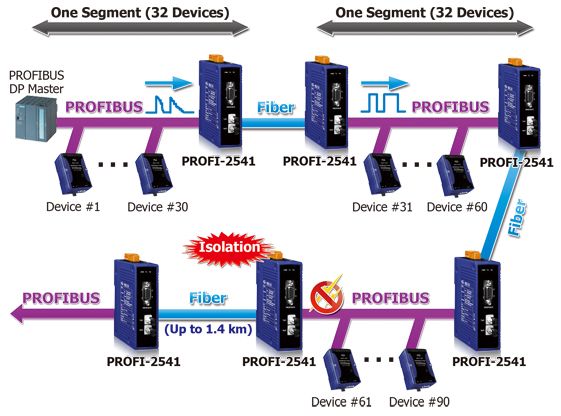
A typical PROFIBUS network consists of a master-slave configuration. The master device, often a PLC or DCS, initiates communication with slave devices, which include sensors, actuators, and other field devices. The network can be configured in various topologies, such as bus, tree, and star.
Master-Slave Communication
In a PROFIBUS network, the master device controls the communication process. It sends out requests to the slave devices, which respond with the necessary data. This cyclical communication ensures that the master has up-to-date information from all connected devices.
Data Exchange
Data exchange in PROFIBUS networks can be categorized into cyclic and acyclic communication:
- Cyclic Communication: This is the regular, time-critical exchange of data between the master and slave devices. It includes process data such as sensor readings and control signals.
- Acyclic Communication: This type of communication is used for non-time-critical data exchange, such as diagnostic information and configuration data.
PROFIBUS Protocol Layers
PROFIBUS operates across several layers of the OSI model, primarily focusing on the Physical, Data Link, and Application layers:
- Physical Layer: PROFIBUS uses RS-485 or fiber optic transmission technology for data transfer. The physical layer defines the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the network.
- Data Link Layer: This layer handles data framing, error detection, and retransmission. The Fieldbus Data Link (FDL) protocol is used to manage data exchange between devices.
- Application Layer: The application layer protocol defines the communication functions and services for data exchange, ensuring interoperability between devices from different manufacturers.
Benefits of PROFIBUS
PROFIBUS offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for industrial automation:
- High-Speed Communication: PROFIBUS DP supports data rates up to 12 Mbps, enabling rapid data exchange in time-sensitive applications.
- Robustness: PROFIBUS PA is designed for use in harsh industrial environments, providing reliable communication even in the presence of electrical noise and other interferences.
- Scalability: PROFIBUS networks can easily scale to include a large number of devices, supporting complex automation systems.
- Interoperability: The standardization of the PROFIBUS protocol ensures compatibility between devices from different manufacturers, facilitating seamless integration.
Conclusion
PROFIBUS is a powerful and versatile communication protocol that plays a critical role in industrial automation. By understanding its working principles, network structure, and benefits, engineers can design and maintain efficient automation systems that meet the demands of modern industrial processes.
For further reading and technical details, please refer to the following sources:
Comments
Post a Comment